|
M. Abdullah Bulbul, Ph.D.Postdoctoral Researcher at University of California, Berkeley
PhD: Bilkent University, Department of Computer Engineering, 2012
(supervised by: Tolga Capin)
|
- Computer Graphics
- Visual Attention
- 3D Displays
- Depth Perception
- Human Computer Interaction
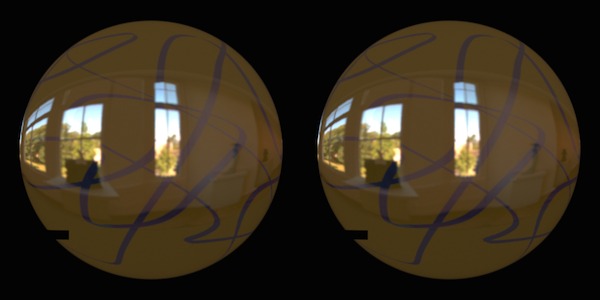
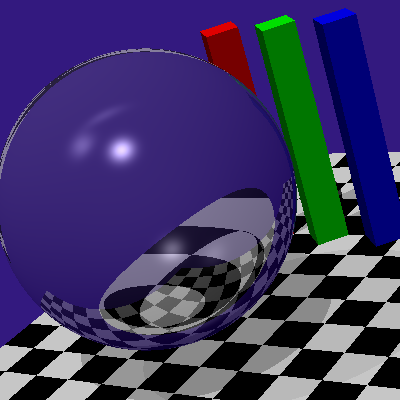
The Perception of Surface Material from Disparity and Focus Cues
We present the effect of focus, stereo disparity, and motion parallax cues on material/glossiness perception. We found a significant effect of each isolated cue on glossiness perception, i.e, in a volumetric display, users gave a higher glossiness rating if the reflections are rendered to their correct depths even with monocular vision.
|
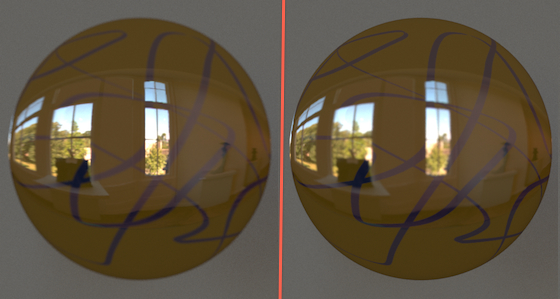 |
Can 3D Shape be Estimated from Focus Cues Alone?
In an experiment, we show convex or concave hinges to the subjects on a volumetric display which is capable of providing near-correct focus cues. All other depth cues were uninformative and the users were able to judge the hinge direction using focus cues alone.
|
 |
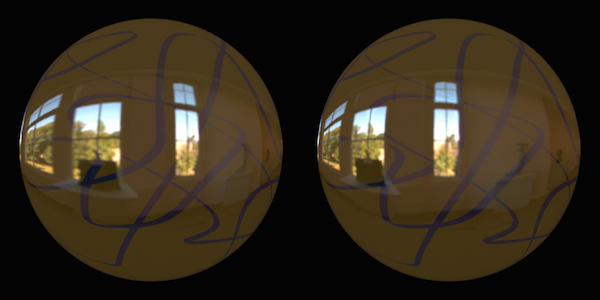
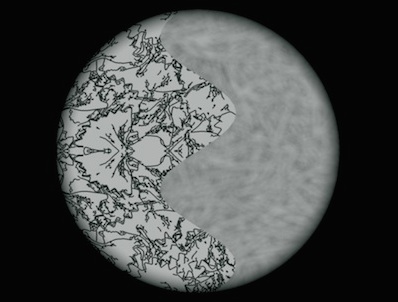
Correct blur and accommodation information is a reliable cue to depth ordering
It is known that blur by itself is an unsigned depth cue (on non-volumetric displays). In this study, we present the effectiveness of blur and accommodation on depth ordering using a volumetric multi-plane display.
|
 |
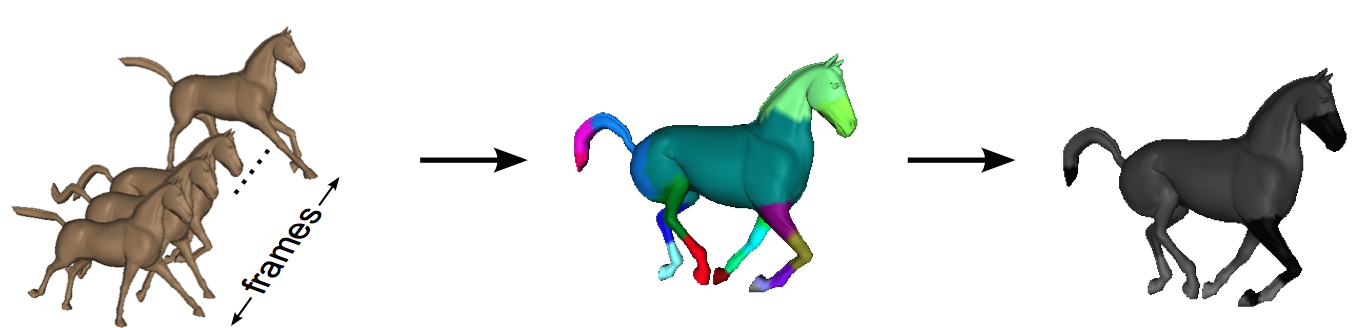
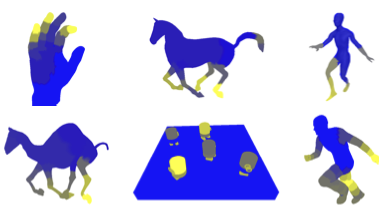
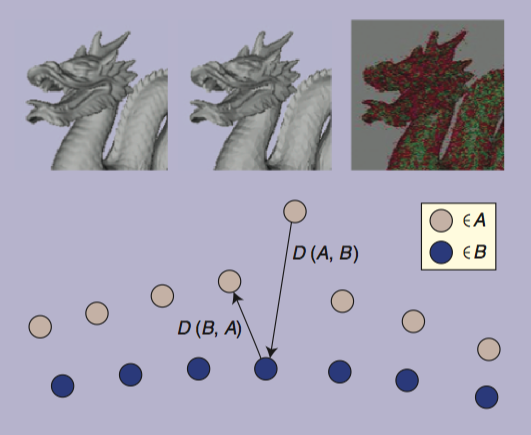
A Clustering-Based Method to Estimate Saliency in 3D Animated Meshes
We present a model to determine the perceptually significant elements in animated 3D scenes using a motion-saliency method. Our model clusters vertices with similar motion-related behaviors. Then each cluster is analyzed as a single unit and representative vertices of each cluster are used to extract the motion-saliency values of each group.
|
 |
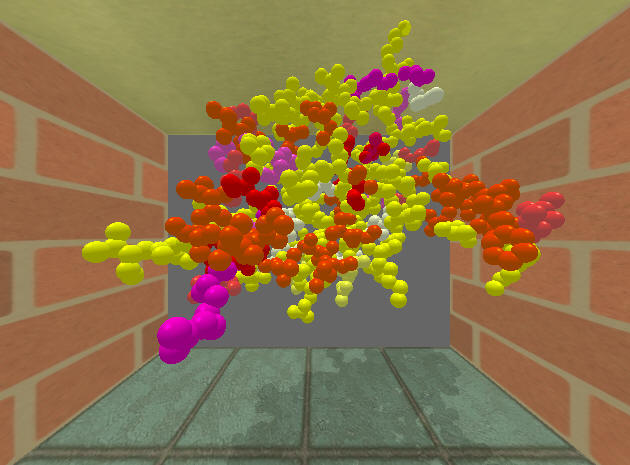
A Framework for Applying the Principles of Depth Perception to Information Visualization
During the visualization of 3D content, using the depth cues selectively to support the design goals and enabling a user to perceive the spatial relationships between the objects are important concerns. In this novel solution, we automate this process by proposing a framework that determines important depth cues for the input scene and the rendering methods to provide these cues.
|
 |
Perceptual Caricaturization of 3D Models
We present a perceptual caricaturization approach practicing the concept of exaggeration, which is very common in traditional art and caricature, on 3D mesh models synthesizing the idea of mesh saliency.
|
 |
Perceptual 3D Rendering Based on Principles of Analytical Cubism
We present a novel approach for cubist rendering of 3D synthetic environments. Rather than merely imitating cubist
paintings, we apply the main principles of analytical cubism to 3D graphics rendering.
|

 |
Assessing Visual Quality of 3-D Polygonal Models
Recent advances in evaluating and measuring the perceived visual quality of three-dimensional (3-D)
polygonal models are presented in this article, which analyzes the general process of objective
quality assessment metrics and subjective user evaluation methods and presents a taxonomy of existing solu-
tions.
|
 |
A Decision Theoretic Approach to Motion Saliency in Computer Animations
We describe a model to calculate saliency of objects due to their motions. In a decision-theoretic fashion, perceptually significant objects inside a scene are detected. We conducted several eye-tracking experiments to practically observe the motion-attention related principles in psychology literature. We also performed some final user studies to evaluate our model and its effectiveness.
|
 |
A Framework for Enhancing Depth Perception in Computer Graphics
This paper introduces a solution for enhancing depth perception in a given 3D computer-generated scene. For this purpose, we propose a framework that decides on the suitable depth cues for a given scene and the rendering methods which provide these cues.
|
 |
Saliency for Animated Meshes with Material Properties
We propose a technique to calculate the saliency of animated meshes with material properties. The saliency computation considers multiple features of 3D meshes including their geometry, material and motion.
|
 |
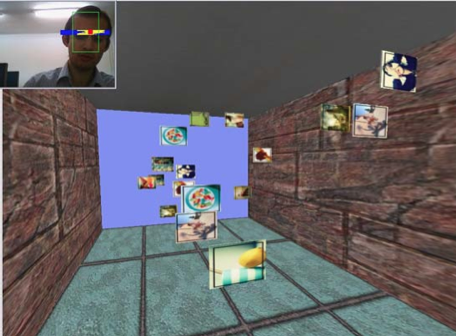
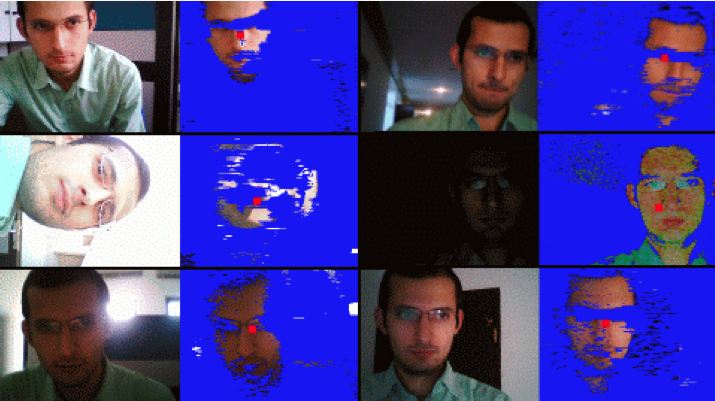
A Color-Based Face Tracking Algorithm for Enhancing Interaction with Mobile Devices
A color-based face tracking algorithm is proposed to be used as a human-computer interaction tool on mobile devices. The solution provides a natural means of interaction enabling a motion parallax effect in applications. The algorithm considers the characteristics of mobile use-constrained computational resources and varying environmental conditions.
|
 |
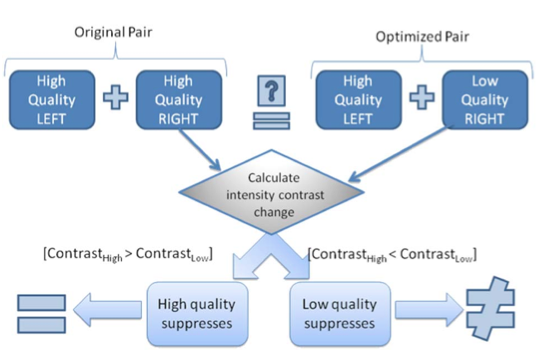
A Perceptual Approach for Stereoscopic Rendering Optimization
We propose a perceptually-based approach for accelerating stereoscopic rendering. This optimization approach is based on the Binocular
Suppression Theory, which claims that the overall percept of a stereo pair in a region is determined by
the dominant image on the corresponding region. We investigate how binocular suppression
mechanism of human visual system can be utilized for rendering optimization.
|
 |
A Face Tracking Algorithm for User Interaction in Mobile Devices
A new face tracking algorithm, and a human-computer interaction technique based on this algorithm, are proposed for use on mobile devices. The face tracking algorithm considers the limitations of mobile use case - constrained computational resources and varying environmental conditions.
|
 |
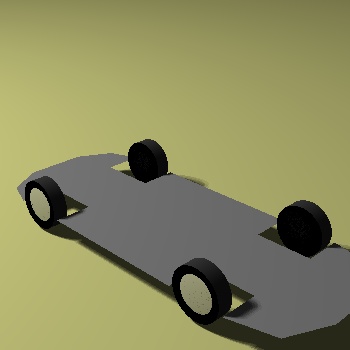
Animation of Boiling Phenomena
We present an efficient method for the simulation of boiling water in this paper. The method is based on
modeling the bubbles and waves as particles. Grid-based approach is
used both for the heating and the fluid surface.
|
 |